PGT-M/A
PGT for monogenetic disorders (PGT-M/A)
Previously known as PGD, PGT-M/A is a technique used to analyze genes in families with a known single gene disorder in which the gene and/or mutation has been confirmed. At Superior A.R.T. we use Karyomapping, to select embryos not affected by the family genetic disease. We can do any diagnosed and confirmed single gene disorder, and they include such genetic disorders as thalassemia, hemophilia, polycystic kidney disease, Huntington’s disease, albinism, color blindness, neurofibromatosis, spinal muscular atrophy, and thousands more.
Who should use PGT-M/A?
Couples where one or both are carriers of a known and confirmed single gene disorder, or who have a child with a genetic disorder
Couples with a child already affected by a disorder (genetic or non-genetic) which is potentially treatable by stem cell therapy. We can do HLA matching (see below).
Couples where one or both are carriers of a balanced chromosomal translocation and want to detect whether balanced embryos are carriers or non-carriers of the translocation
Family history of a genetic condition
Karyomapping
Karyomapping is the latest technology for preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disorders. Unlike other PGT-M tests which usually take months to finish the test workup, Karyomapping only requires 1-3 weeks to complete a test workup. It is considered highly accurate, has a greater than 95% reliability, and allows PGT-A at the same time. With Karyomapping, DNA fingerprints of embryos and family members will be compared to determine which embryos are free from the disorder.
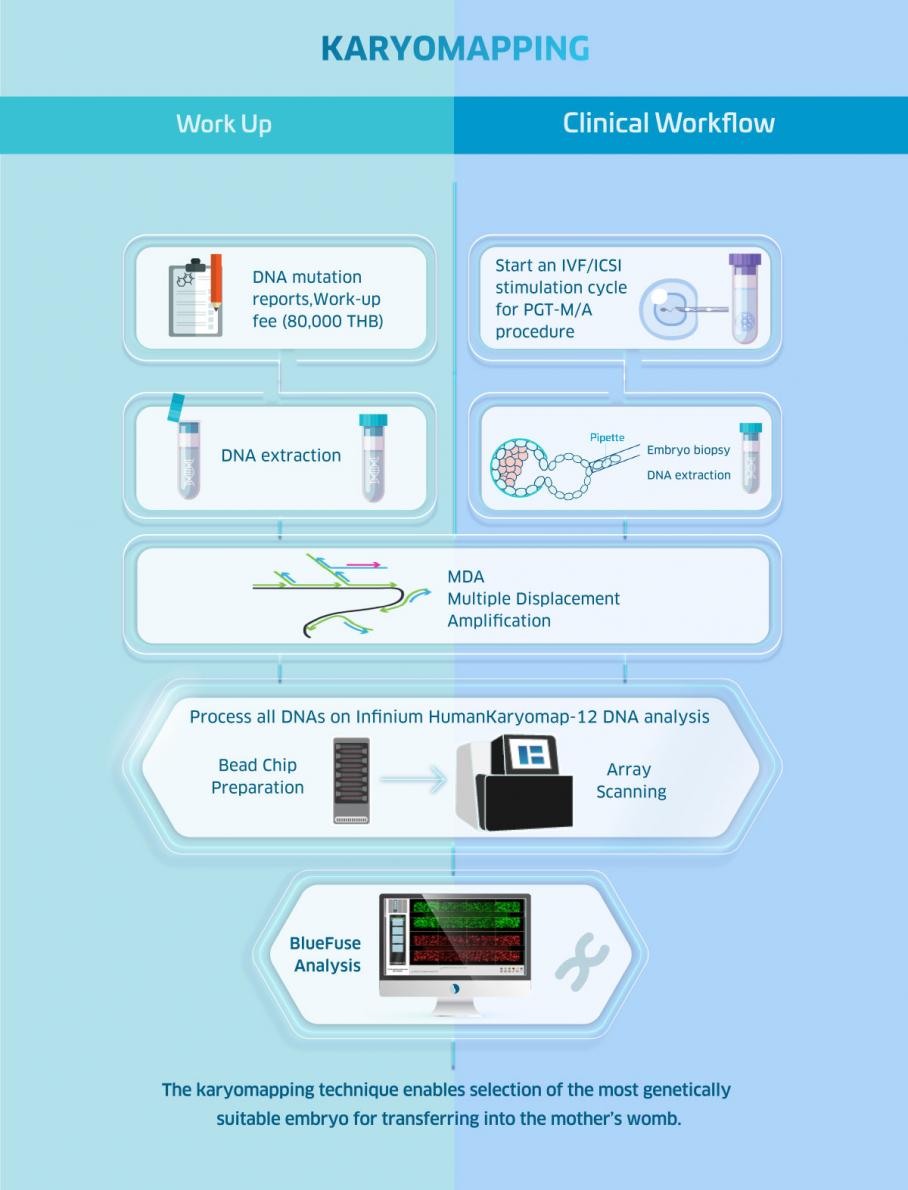
PGT-M – PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) with NGS (Next Generation Sequencing)?
At Superior A.R.T. we previously used the PCR technique for PGT-M for the single gene disorders (and/or HLA Matching – see below), and we did it in combination with NGS for PGT-A, comprehensive chromosome screening. Now we use karyomapping for most new cases, but still use PCR for some older cases, and a few new cases we cannot do using karyomapping. The ‘combination’ testing of PGT-M/A using PCR/NGS is done on a single biopsy of cells from an embryo, and allowed couples to know whether the embryos had genetic and/or chromosomal disorders. After the first step of DNA extraction, part of the extract was used for NGS, and part for the PCR.
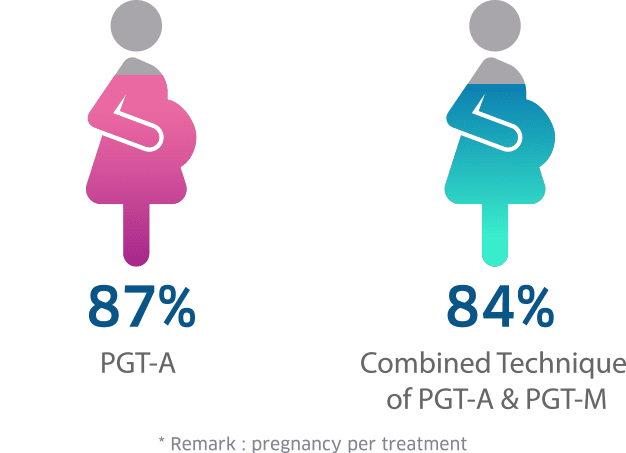
PGT-A and PGT-M Success Rate at Superior A.R.T.
HLA Matching?
A couple who have an existing child with a disorder, genetic or non-genetic, that is potentially treatable by stem cell therapy, can have another child (free of the disorder if it is genetic disorder such as thalassemia) who is an exact HLA match (tissue compatible) to the existing child. At birth of the new child cord blood can be collected, stem cells harvested, and these used to treat the existing affected child. This treatment is very successful since the HLA match is a 100% genetic match. We were the first clinic in Asia to use this technique to successfully cure an existing child.
While we can screen for any diagnosed confirmed single gene disorder, there is a list of some of the disorders we have screened for;
PGT-M (PCR) cases at Superior A.R.T. 2007-Present
| GENETIC DISORDER | No. of cycle |
|---|---|
| Blood disorder | |
| Beta-thalassemia (HBB gene) | 108 |
| Beta-thalassemia and HLA matching | 109 |
| Alpha-thalassemia (HBA1,HBA2 gene) | 152 |
| Alpha-thalassemia and HLA matching | 4 |
| Sickle cell anemia (HBB gene) | 9 |
| Sickle cell anemia and HLA matching | 3 |
| Hemophilia A (FVIII) | 9 |
| Hemophilia B (FIX) | 6 |
| Glanzmann’s thombasthenia (GT;ITGA2B gene) | 2 |
| Rh-negative | 1 |
| Hereditary spherocytosis (HS;SPTB gene) | 2 |
| Neurodegenerative disorder | |
| Spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2;ATXN2 gene) | 2 |
| Krabbe disease (GALC gene) | 3 |
| Huntington disease (PRNP gene) | 1 |
| Metachromatic leukodystrophy (ARSA gene) | 1 |
| Epileptic encephalopathy (CACNA1A gene) | 1 |
| Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (PANK2 gene) | 1 |
| Charcot-marie-tooth disease (MFN2,PMP22,IGHMBP2 genes) | 4 |
| Mitochondrial recessive ataxia syndrome (POLG gene) | 2 |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS;TARDBP gene) | 1 |
| Cockayne syndrome (ERCC8 gene) | 1 |
| Microcephaly (ASPM gene) | 1 |
| Cancer predisposition | |
| Von hipple lindau Disease (VHL gene) | 4 |
| Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1 gene) | 2 |
| Leukemia (HLA match) | 1 |
| Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2A;RET gene) | 2 |
| Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (SMARCB1 gene) | 1 |
| Muscular dystrophy / Dysfunction syndrome | |
| Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD gene) | 14 |
| Becker muscular dystrophy (DMD gene) | 1 |
| Myotonic dystrophy (DMPK gene) | 1 |
| Spinal muscular atrophy 1 (SMN1 gene) | 17 |
| Alpha smooth muscle actin (ACTA2 gene) | 1 |
| Muscular dystrophy / Dysfunction syndrome (PLEC gene) | 1 |
| Multisystem disorder | |
| Cystic fibrosis (CFTR gene) | 3 |
| Tuberous sclerosis (TSC2 gene) | 5 |
| Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type 1 (PKD1,PKD2 gene) | 17 |
| Autosomal recessive polycystic kdney disease (PKHD1 gene) | 2 |
| Marfan syndrome (FBN1 gene) | 3 |
| Schaaf-Yang syndrome (MAGEL2 gene) | 1 |
| Prader-Willi syndrome (SNRPN gene) | 2 |
| Cohen syndrome (VPS13b gene) | 1 |
| Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (ABCC8 gene) | 2 |
| Nephrotic syndrome (NPHS1 gene) | 1 |
| Dyskeratosis congenital (RTEL gene) | 1 |
| Menkes disease (ATP7A gene) | 2 |
| Fragile X syndrome (FMR1 gene) | 1 |
| Joubert syndrome (CC2D2A gene) | 1 |
| Loss of sensing | |
| Color blindness | 2 |
| Deafness digenic (GJB2,MYO15A,TMIE) | 3 |
| Retinitis pigmentosa (GUCA1B,USH2A,CRB1) | 3 |
| Cone-rod dystrophy (RPGRIP gene) | 1 |
| Skin / Hair / Eye disease | |
| Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia (JEB-PA) | 1 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa (COL7A1,ITGB4) | 4 |
| Epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (KRT9 gene) | 1 |
| Oculocutaneous albinism Type 2 (OCA2,TYR genes) | 5 |
| Ectodermal dysplasia (EDA gene) | 1 |
| Cone-rod dystrophy (GUCY2D,CACNA1F,BBS4 genes) | 3 |
| Metabolic disease | |
| Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTC) | 9 |
| Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 12 (Zellweger syndrome) (PEX12 gene) | 1 |
| Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD gene) | 6 |
| Sulfite oxidase deficiency (SUOX gene) | 2 |
| Pompe disease (GAA gene) | 2 |
| Methylmalonic aciduria (MUT gene) | 1 |
| Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria (MMACHC gene) | 2 |
| Homocystinuria (MTHFR gene) | 1 |
| Congenital Adrenal hyperplasia (CAH gene) | 2 |
| Phenylketonuria (PAH gene) | 5 |
| Citrullinemia (SLC25A13 gene) | 1 |
| Propionicacidemia (PCCB gene) | 2 |
| Osteoblastic differentiation/ Skeletal morphogenesis | |
| Cleidocranical dysplasis (RUNX2 gene) | 1 |
| Osteogenesis imperfecta (COL1A1,COL2A1 genes) | 4 |
| Multiple exostoses (EXT1,EXT2 genes) | 2 |
| Hypophosphatemic rickets (PHEX gene)Hereditary multiple exostoses | 2 |
| Achondroplasia (FGFR3 gene) | 1 |
| Others | |
| Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) (IL2RG,btk genes) | 4 |
| HLA-B27 | 7 |
| Carrier and non-carrier translocation | 9 |
| Cardiomyopathy (MYBPC3 gene) | 3 |
| Thyroid dyshormonogenesis (DUOX2 gene) | 1 |
| Androgen insensitivity (AR gene) | 2 |
| 604 | |







