Biopsy & PGT
Biopsy
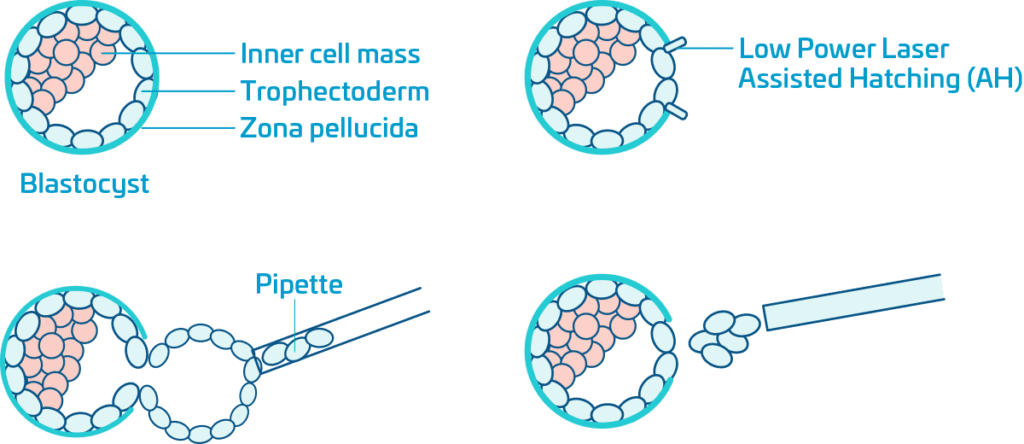
At the blastocyst stage of embryo development, usually on day 5 or day 6, the blastocyst is composed of three main parts, the zona pellucida (the “shell”), the inner cell mass (destined to become the fetus) and the trophectoderm (extra-embryonic tissue that becomes part of the placenta and membranes).
Normally on about day 6 of embryo culture the expanding blastocyst will form a hole in the zona pellucida and the rapidly expanding trophectoderm cells will herniate (go out the hole) and eventually the complete blastocyst will be fully hatched and ready to implant in wall of the mothers uterus.
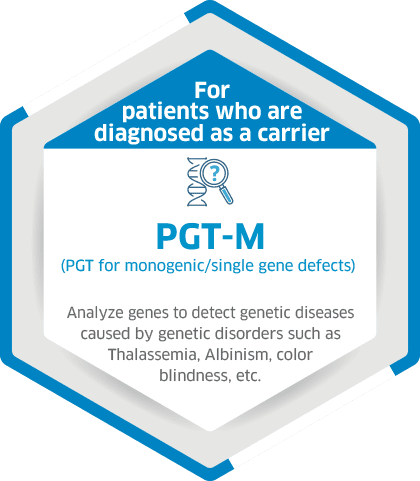
Assisted Hatching (AH) to allow this hatching to begin a little earlier, on day 3 or day 4 of embryo culture we make a small hole in the zona pellucida using a low power precise laser. On day 5 or day 6 we can biopsy (remove) a few cells from the hatching trophectoderm. The cells are used for PGT-A or PGT-M screening. The expanding trophectoderm quickly repairs and the blastocyst continues to grow until frozen using vitrification.