PESA/TESE for ICSI
What is PESA/TESE?
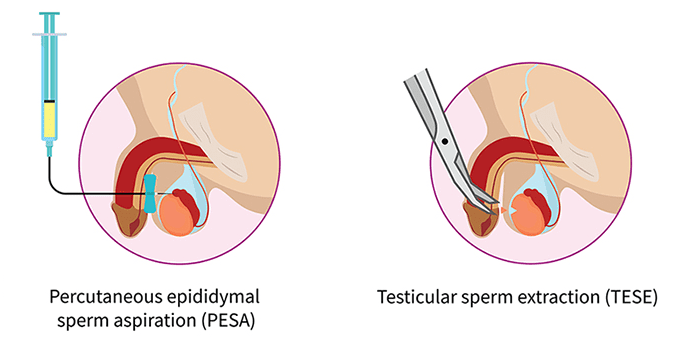
PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration)
and TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction)
are methods used to retrieve sperm directly from the male reproductive organs. These procedures are typically indicated when no sperm is found in the ejaculate or when semen cannot be collected through normal ejaculation.
PESA involves the insertion of a fine needle through the scrotal skin to aspirate sperm directly from the epididymis.
TESE is a minor surgical procedure in which a small incision is made in the scrotum to access the testicle, allowing tissue to be collected from the seminiferous tubules for laboratory examination to identify the presence of sperm.
Eligibility Criteria for PESA/TESE
These procedures are suitable for men with the following conditions:
Procedure Overview
Possible Complications
Preparation Before the Procedure
Following PESA or TESE treatment, the collected sperm will be processed and used in intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), a form of in vitro fertilization.
Article by
SIRICHET ANEKPORNWATTANA, M.D.
Obstetrician & Gynecologist, Reproductive Endocrinologist and Infertility Specialist







